Understanding Dementia Tests: A Comprehensive Guide
Dementia is a complex condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Early detection and diagnosis are crucial for effective management and care. In this article, we will explore the various tests used to assess and diagnose dementia, providing valuable insights into the process and importance of testing. Whether you are a caregiver, healthcare professional, or someone concerned about cognitive health, understanding dementia tests is essential for proactive healthcare.

Introduction to Dementia and its Impact
Dementia is a progressive neurological condition that impairs cognitive function, affecting memory, reasoning, and communication. It can significantly impact daily life and independence, making early detection vital for timely intervention and support. Dementia can result from various underlying causes, including Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, and Lewy body dementia.
The Importance of Dementia Testing
Dementia testing plays a crucial role in identifying cognitive decline, determining the type and stage of dementia, and developing personalized care plans. Early diagnosis allows for better management of symptoms, access to appropriate treatments, and support services. Additionally, understanding the specific type of dementia can help tailor interventions to address individual needs effectively.
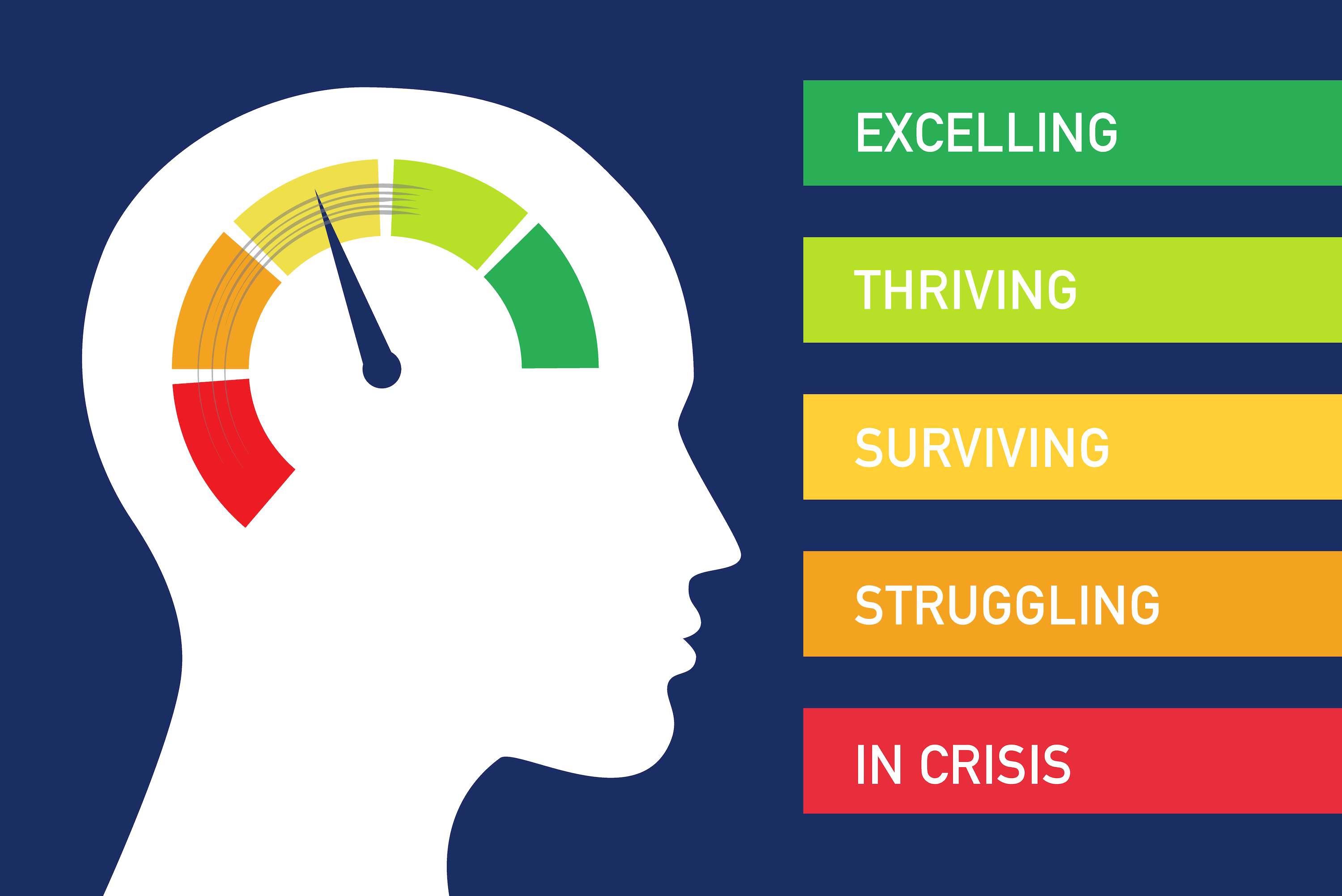
Common Dementia Tests and Assessments
1. Cognitive Assessments: These tests evaluate memory, language, attention, and problem-solving skills to assess cognitive function and detect changes indicative of dementia. Examples include the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA).
2. Brain Imaging: Imaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans can reveal structural changes in the brain associated with dementia, aiding in diagnosis and monitoring progression. PET scans can also detect abnormal protein deposits characteristic of certain types of dementia, like Alzheimer's disease.
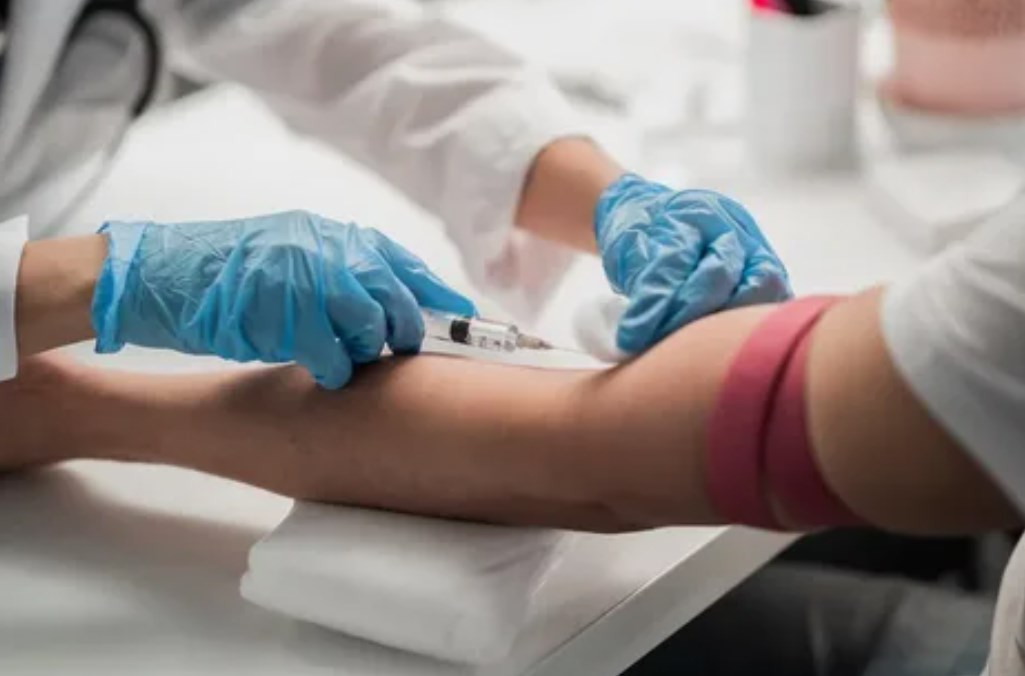
3. Blood Tests: Blood tests may help identify underlying conditions that contribute to cognitive decline, such as vitamin deficiencies, thyroid dysfunction, or infections. Genetic testing can also provide insights into the risk of developing hereditary forms of dementia.
Diagnostic Criteria and Guidelines
Diagnosing dementia involves a comprehensive evaluation of cognitive function, medical history, and physical examination. Healthcare professionals follow established diagnostic criteria, such as those outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) or the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), to ensure accurate and consistent diagnosis.
Challenges and Considerations in Dementia Testing
While dementia testing is essential, it is not without challenges. Factors such as cultural differences, language barriers, and variations in symptom presentation can complicate the diagnostic process. Moreover, the stigma associated with dementia may deter individuals from seeking testing and support, highlighting the need for education and awareness.

The Role of Caregivers and Healthcare Professionals
Caregivers and healthcare professionals play a crucial role in facilitating dementia testing and supporting individuals throughout the diagnostic journey. By providing emotional support, guidance, and access to resources, they empower individuals to seek timely evaluation and appropriate care.











全部评论